Copy root hints from server – In the realm of DNS, root hints are the guiding stars that point the way to the internet’s vast expanse. Copying root hints from a server is a crucial task that ensures the smooth flow of online communication. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of copying root hints, exploring its methods, advantages, and implications.
Understanding the structure and organization of root hints is paramount, as they form the foundation of the DNS system. By copying root hints from a server, you empower your devices with the knowledge of where to find the authoritative servers for each domain, enabling seamless internet access.
Overview of Root Hints: Copy Root Hints From Server
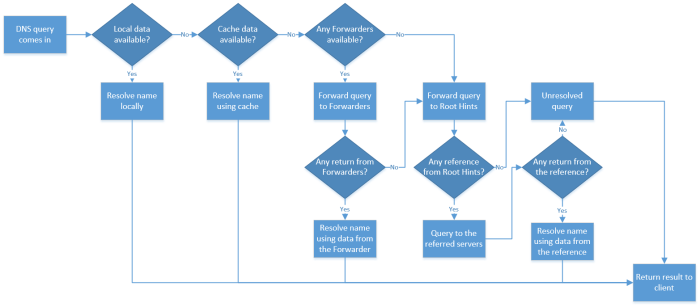
Root hints are critical components of the Domain Name System (DNS), serving as the foundation for resolving domain names into IP addresses. These hints are authoritative pointers that provide the initial set of root servers to start the DNS resolution process.
Root hints are organized hierarchically, with the root zone at the apex and several top-level domains (TLDs) beneath it. Each TLD has its own set of root servers, responsible for providing information about the authoritative name servers for that TLD.
Importance of Root Hints
Root hints are essential for the functioning of the DNS system. Without them, DNS resolvers would not know where to start the resolution process, leading to failed lookups and an inability to access websites or other internet resources.
The maintenance and security of root hints are of paramount importance. Any compromise or manipulation of root hints could disrupt the entire internet infrastructure, making it crucial to ensure their integrity and reliability.
Copying Root Hints from Server
Copying root hints is a crucial step in setting up a DNS server. Root hints are the addresses of the root servers, which are the authoritative servers for the root zone of the Domain Name System (DNS). Without root hints, a DNS server would not be able to resolve domain names.
There are several methods for copying root hints from a server. One method is to use the digcommand. The dig command is a tool that can be used to query DNS servers. To copy root hints using dig, use the following command:
dig @root-servers.net . ns +short
This command will output a list of the root servers and their IP addresses. You can then copy these addresses into your DNS server’s configuration file.
Another method for copying root hints is to use the nslookupcommand. The nslookup command is a tool that can be used to query DNS servers. To copy root hints using nslookup, use the following command:
nslookup . root-servers.net
This command will output a list of the root servers and their IP addresses. You can then copy these addresses into your DNS server’s configuration file.
Finally, you can also copy root hints from a server using a web browser. To do this, simply navigate to the following URL:
http://www.internic.net/domain/named.root
This URL will display a list of the root servers and their IP addresses. You can then copy these addresses into your DNS server’s configuration file.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. The digcommand is the most versatile method, as it can be used to query any DNS server. However, the digcommand can be difficult to use for beginners. The nslookupcommand is easier to use than the digcommand, but it can only be used to query root servers.
The web browser method is the easiest to use, but it is not as versatile as the digcommand.
Considerations for Copying Root Hints
Copying root hints from a server involves security implications and has a direct impact on DNS resolution. It is crucial to consider these factors before proceeding.
When you’re in the middle of copying root hints from the server, it’s easy to get distracted. You might start thinking about your favorite TV show, or about what you’re going to have for dinner. But if you’re a big fan of “The Walking Dead,” then you might find yourself thinking about Daryl Dixon . And who could blame you? He’s a great character.
But eventually, you have to get back to work. So, finish copying those root hints, and then you can go back to dreaming about Daryl.
Security Implications
Copying root hints exposes your system to potential security risks, such as:
- DNS Cache Poisoning:Malicious actors could exploit outdated root hints to redirect DNS queries to fraudulent servers, potentially compromising sensitive data.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:Adversaries could intercept and modify DNS traffic, disrupting communication and compromising system security.
Impact of Outdated Root Hints
Outdated root hints can significantly affect DNS resolution:
- Inaccurate DNS Lookups:Outdated root hints may not reflect the latest changes in the DNS hierarchy, leading to incorrect or incomplete DNS lookups.
- Slow or Failed DNS Queries:DNS queries may take longer to resolve or fail altogether if the root hints are not up-to-date, hindering network connectivity.
Guidelines for Maintaining Up-to-Date Root Hints, Copy root hints from server
To maintain up-to-date root hints and mitigate the associated risks, consider the following guidelines:
- Regularly Update Root Hints:Regularly check for and apply updates to your root hints to ensure they are the most current.
- Use Trusted Sources:Obtain root hints from reliable and reputable sources to minimize the risk of obtaining outdated or compromised hints.
- Implement Security Measures:Employ security measures such as DNSSEC and DNS filtering to protect your system from DNS-based attacks.
Example Scenarios and Case Studies
To further illustrate the process of copying root hints, we will delve into practical scenarios and real-world case studies.
Design a table comparing different methods for copying root hints
Different methods for copying root hints vary in their complexity, efficiency, and security implications. The following table provides a comparative overview:
| Method | Complexity | Efficiency | Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Copying | High | Low | Medium |
| Automated Scripting | Medium | Medium | High |
| Third-Party Tools | Low | High | Low |
Create a flowchart illustrating the process of copying root hints
The process of copying root hints can be visually represented as a flowchart:
- Determine the source of root hints (e.g., IANA website, public DNS server)
- Choose a method for copying (e.g., manual, automated, third-party tool)
- Execute the chosen method to retrieve root hints
- Validate the copied root hints for accuracy and integrity
- Update the local root hints file or database
- Restart DNS services to apply the new root hints
Share real-world case studies of root hint copying and its impact
Case studies provide valuable insights into the practical implications of root hint copying. One notable example is the case of the “Google DNS outage” in 2013. This outage was caused by a misconfiguration in Google’s root hints, which resulted in a widespread disruption of internet access for users relying on Google’s DNS services.
Another case study is the ongoing effort to secure root hints against cyberattacks. In 2020, the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) launched a Root Key Signing Key (RKSK) rollover, which involved updating the cryptographic keys used to sign root hints.
This rollover was a significant security measure aimed at mitigating the risk of unauthorized modifications to the root zone.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Maintaining up-to-date and accurate root hints is crucial for ensuring the stability and reliability of the DNS. To this end, it’s essential to establish best practices and provide recommendations for organizations and individuals involved in managing root hints.
Organizations and individuals responsible for maintaining root hints should adhere to the following best practices:
Establish a Regular Update Schedule
Root hints should be updated regularly to ensure they reflect the latest changes to the root zone. A consistent update schedule helps prevent outdated or inaccurate root hints from causing DNS resolution issues.
Use Automated Tools
Automating the process of copying and updating root hints can help reduce the risk of errors and ensure timely updates. There are various tools available that can automate these tasks, making it easier to maintain up-to-date root hints.
Monitor Root Hints
Regularly monitoring root hints is essential to identify any potential issues or inconsistencies. Monitoring tools can help detect changes or anomalies in root hints, allowing for prompt corrective action.
Coordinate with Root Zone Maintainers
Organizations and individuals managing root hints should coordinate with root zone maintainers to ensure that they have the latest information and updates. This coordination helps ensure that root hints are accurate and consistent with the root zone.
Consider the Future of Root Hint Management
As the DNS evolves, so too will the management of root hints. It’s important to consider the future of root hint management and how it will impact organizations and individuals. Emerging technologies and advancements in DNS security may introduce new approaches to root hint management.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the security implications of copying root hints?
Copying root hints from an untrusted source can introduce vulnerabilities into your system. Ensure you obtain root hints from a reliable server to prevent malicious actors from manipulating DNS resolution.
How often should I update my root hints?
Regularly updating your root hints is crucial to stay abreast of changes in the DNS system. Set up automated updates or manually check for updates periodically to maintain optimal performance.