Having an extra electron crossword delves into the fascinating realm of atomic structure and chemical properties, unraveling the intricate interplay between electrons and the behavior of elements. This article embarks on a journey to explore the profound impact of an extra electron on the fundamental characteristics and reactivity of atoms and ions.
Delving deeper, we will uncover the consequences of an extra electron on atomic number, atomic mass, and electron configuration. We will examine how this additional electron shapes the chemical properties of elements, including their oxidation states, bonding behavior, and ability to participate in chemical reactions.
Having an Extra Electron: Having An Extra Electron Crossword
In the realm of atomic chemistry, the presence of an extra electron significantly alters the properties and behavior of an atom or ion. Understanding the implications of having an extra electron is crucial for comprehending the fundamental principles of chemistry and its applications.
Definition and Explanation
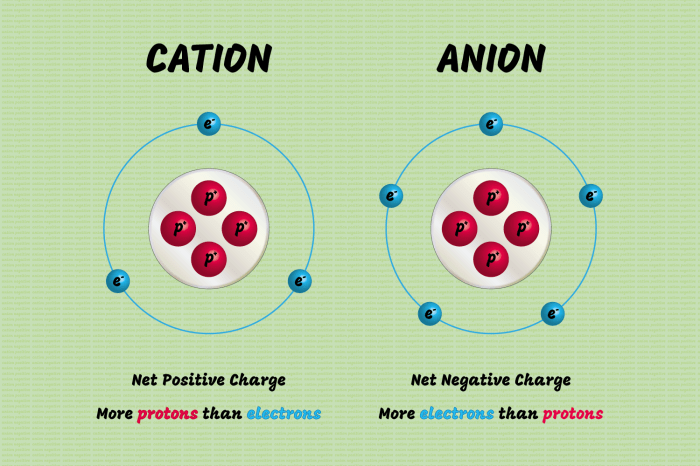
An extra electron refers to an additional negative charge carried by an atom or ion beyond its normal electron configuration. This occurs when the number of electrons exceeds the number of protons in the atomic nucleus, resulting in a net negative charge.
The presence of an extra electron affects the atomic number, atomic mass, and electron configuration of the atom or ion.
- Atomic Number:The atomic number remains unchanged as the extra electron does not alter the number of protons in the nucleus.
- Atomic Mass:The atomic mass increases slightly due to the additional electron’s mass, although the change is negligible.
- Electron Configuration:The extra electron occupies the lowest available energy level, modifying the electron configuration and affecting the atom’s or ion’s chemical properties.
Examples of elements or ions with an extra electron include:
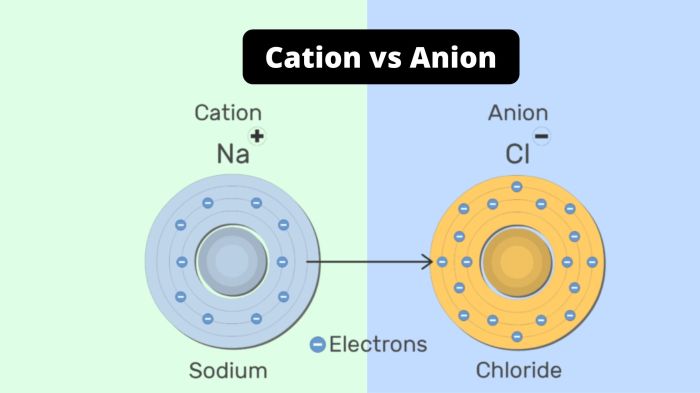
- Sodium ion (Na+): Sodium loses an electron to achieve a stable electron configuration, resulting in a positive ion with an extra electron in its outermost shell.
- Chloride ion (Cl–): Chlorine gains an electron to complete its outermost shell, forming a negative ion with an extra electron.
Chemical Properties
The presence of an extra electron significantly influences the chemical properties of atoms or ions.
- Reactivity:Atoms or ions with an extra electron are generally more reactive as they have a weaker attraction to their nucleus.
- Oxidation States:The extra electron can lead to variable oxidation states, allowing the atom or ion to participate in a wider range of chemical reactions.
- Bonding Behavior:The extra electron affects the bonding behavior of the atom or ion, making it more likely to form ionic or covalent bonds.
Examples of chemical reactions involving species with an extra electron include:
- Sodium and chlorine reaction:Sodium reacts with chlorine to form sodium chloride (NaCl), an ionic compound where sodium loses its extra electron to chlorine.
- Hydrogen and oxygen reaction:Hydrogen and oxygen react to form water (H 2O), a covalent compound where the extra electrons from hydrogen atoms form covalent bonds with oxygen.
Physical Properties, Having an extra electron crossword
Substances with an extra electron can exhibit unique physical properties.
- Color:The extra electron can absorb or emit light of specific wavelengths, resulting in characteristic colors.
- Magnetism:The unpaired extra electron can contribute to paramagnetism, where the substance is attracted to magnetic fields.
- Electrical Conductivity:Substances with mobile extra electrons can exhibit electrical conductivity, allowing them to conduct electricity.
Examples of materials with extra electrons and their associated physical properties include:
- Copper:Copper’s extra electron contributes to its reddish color and high electrical conductivity.
- Oxygen:Oxygen’s two unpaired extra electrons make it paramagnetic and contribute to its characteristic blue color.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of an extra electron in an atom?
An extra electron alters the atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties of an atom, influencing its reactivity, bonding behavior, and ability to participate in chemical reactions.
How does an extra electron affect the chemical properties of an element?
The presence of an extra electron can alter an element’s oxidation state, making it more likely to form ions and participate in redox reactions. It can also influence the element’s bonding behavior, affecting its ability to form different types of bonds.
Are there any practical applications of substances with extra electrons?
Substances with extra electrons find applications in various fields, including electronics, catalysis, and energy storage. For instance, semiconductors with extra electrons are essential components in electronic devices, while materials with extra electrons can serve as catalysts in chemical reactions.