Darwin’s theory of evolution concept map answer key offers a comprehensive understanding of the key principles, evidence, and impact of Darwin’s groundbreaking theory. This guide provides a clear and concise overview of the concepts, allowing readers to grasp the essence of Darwin’s evolutionary framework.
Through a detailed examination of natural selection, adaptation, common ancestry, and the evolution of humans, this guide unravels the intricate mechanisms that drive the diversity of life on Earth. It explores the strengths and weaknesses of Darwin’s theory, highlighting its enduring influence on scientific thought.
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution: Darwin’s Theory Of Evolution Concept Map Answer Key

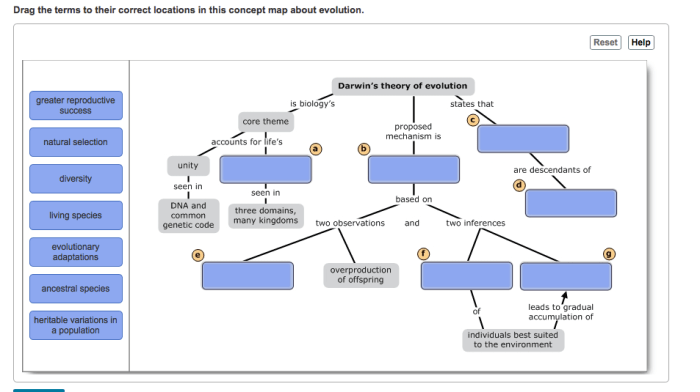
Darwin’s theory of evolution is a scientific theory that explains the diversity of life on Earth. It is based on the idea that all living things have descended from a common ancestor, and that over time, species change through a process called natural selection.
Darwin’s theory is supported by a wide range of evidence, including the fossil record, comparative anatomy, and molecular biology. It has revolutionized our understanding of the natural world and has had a profound impact on scientific thought.
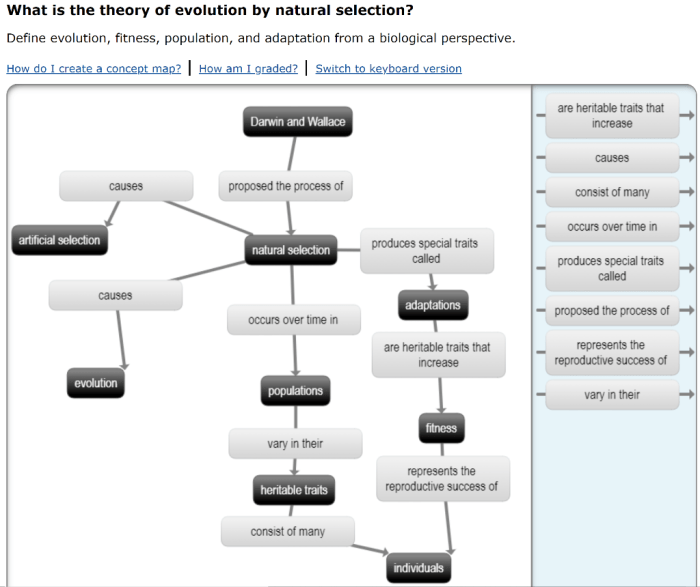
Natural Selection, Darwin’s theory of evolution concept map answer key
Natural selection is the driving force behind evolution. It is a process that favors individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment. These individuals are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring.
Natural selection can lead to the evolution of new species, as well as the extinction of others. It is a powerful force that has shaped the history of life on Earth.
Adaptation
An adaptation is a trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment. Adaptations can be physical, behavioral, or physiological.
Some examples of adaptations include:
- The thick fur of polar bears, which helps them stay warm in cold climates
- The long, sharp claws of eagles, which help them catch and kill prey
- The ability of some plants to produce toxins that deter herbivores
Common Ancestry
The concept of common ancestry states that all living things have descended from a common ancestor. This means that all organisms, from bacteria to humans, share a common evolutionary history.
There is a great deal of evidence to support the concept of common ancestry, including:
- The fossil record
- Comparative anatomy
- Molecular biology
Evolution of Humans
Humans are a relatively recent species, having evolved from ape-like ancestors around 6 million years ago. The evolutionary history of humans is a complex one, but it is well-supported by the fossil record and genetic evidence.
Some of the key milestones in human evolution include:
- The evolution of bipedalism, or walking upright
- The development of a larger brain
- The evolution of language
Criticisms of Darwin’s Theory
Darwin’s theory of evolution has been criticized by some, but it remains the most widely accepted scientific explanation for the diversity of life on Earth.
Some of the main criticisms of Darwin’s theory include:
- The lack of a complete fossil record
- The apparent complexity of some organisms
- The difficulty in explaining the origin of life
However, these criticisms have been addressed by scientists, and Darwin’s theory has been modified and refined over time to account for new evidence.
Query Resolution
What are the key principles of Darwin’s theory of evolution?
The key principles include variation, inheritance, natural selection, and adaptation.
How does natural selection work?
Natural selection favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproduction in a given environment.
What is the evidence for common ancestry?
Evidence includes homologous structures, genetic similarities, and fossil records.