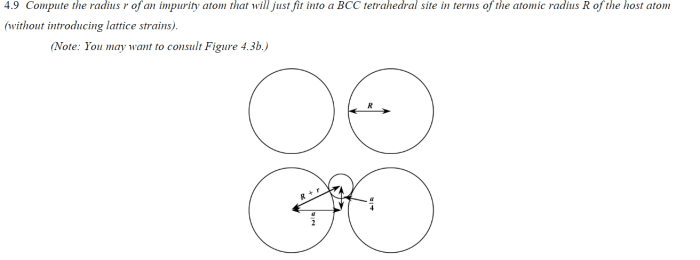
Compute the radius r of an impurity atom in crystal lattices, delving into the fascinating realm of materials science and engineering. This discourse unveils the intricacies of impurity atoms, their impact on crystal structures, and the methodologies employed to determine their radius.
Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey through the world of materials and their fundamental building blocks.
The exploration begins with a comprehensive understanding of impurity atoms and their diverse effects on crystal structures. We delve into the methods used to compute the radius of impurity atoms, examining their assumptions and limitations. Moreover, the factors influencing the accuracy of these calculations are meticulously analyzed.
1. Basic Concepts: Compute The Radius R Of An Impurity Atom
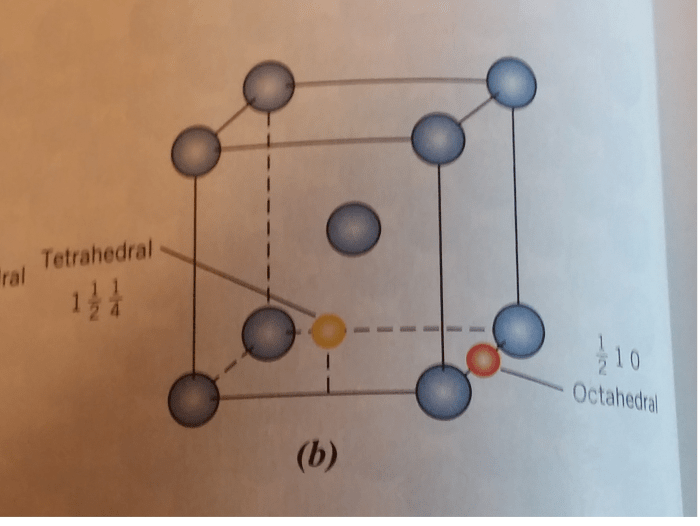
In a crystal lattice, an impurity atom is an atom that differs from the host atoms in the lattice. Impurity atoms can be either substitutional or interstitial.
Substitutional impurity atoms replace a host atom in the lattice, while interstitial impurity atoms occupy the spaces between the host atoms.
Impurity atoms can have a significant impact on the properties of a material. For example, they can affect the electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and mechanical strength of a material.
Types of Impurity Atoms
- Substitutional impurity atoms: These atoms replace a host atom in the lattice. They can be either smaller or larger than the host atoms.
- Interstitial impurity atoms: These atoms occupy the spaces between the host atoms. They are typically smaller than the host atoms.
- Vacancy defects: These are defects in the crystal lattice where an atom is missing.
Effects of Impurity Atoms on Crystal Structure, Compute the radius r of an impurity atom
The presence of impurity atoms in a crystal lattice can disrupt the regular arrangement of the atoms. This can lead to the formation of defects in the lattice, such as dislocations and grain boundaries.
Impurity atoms can also affect the electronic properties of a material. For example, they can introduce energy levels into the band gap of a semiconductor.
2. Computing the Radius of an Impurity Atom
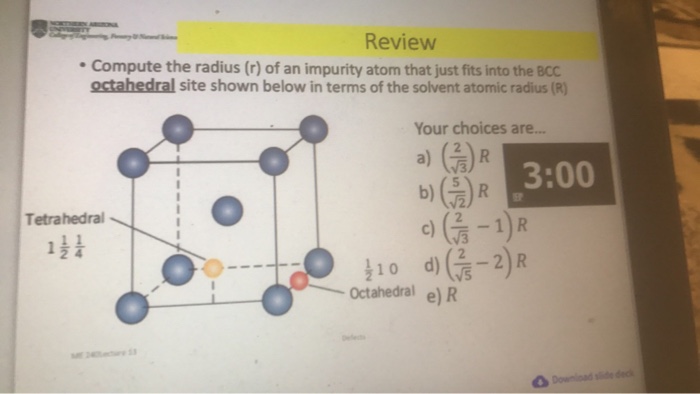
The radius of an impurity atom is a measure of its size. It can be computed using a variety of methods, including:
- The Bragg-Williams approximation: This is a simple method that assumes that the impurity atoms are randomly distributed in the lattice.
- The Vegard-Kapustinskii equation: This is a more accurate method that takes into account the interactions between the impurity atoms and the host atoms.
- Density functional theory (DFT): This is a computational method that can be used to calculate the radius of an impurity atom with high accuracy.
Assumptions and Limitations of These Methods
The Bragg-Williams approximation is a simple method, but it is not very accurate. The Vegard-Kapustinskii equation is more accurate, but it is only valid for small impurity concentrations.
DFT is the most accurate method, but it is also the most computationally expensive.
Factors that Influence the Accuracy of the Computed Radius
The accuracy of the computed radius depends on a number of factors, including:
- The type of impurity atom: The radius of an impurity atom depends on its size and charge.
- The concentration of impurity atoms: The radius of an impurity atom can be affected by the concentration of impurity atoms in the lattice.
- The temperature: The radius of an impurity atom can be affected by the temperature of the lattice.
Query Resolution
What is an impurity atom?
An impurity atom is an atom of a different element that is present in a crystal lattice, altering its composition and properties.
Why is it important to compute the radius of an impurity atom?
The radius of an impurity atom influences the properties of the crystal lattice, such as its strength, electrical conductivity, and optical properties.
What methods are used to compute the radius of an impurity atom?
Various methods are employed, including X-ray diffraction, neutron scattering, and theoretical calculations.