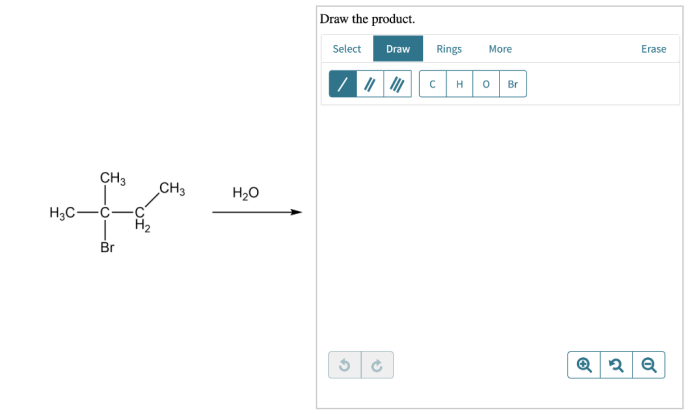
Draw structures for the organic products of the reaction below. – In the realm of organic chemistry, understanding the structures of organic products is crucial for comprehending reaction mechanisms and predicting product properties. This article delves into the intricacies of drawing structures for the organic products of a given reaction, providing a comprehensive guide to accurately represent the molecular architecture of these compounds.
Through a systematic approach, we will explore the fundamental principles of structural representation, delve into the physical and chemical properties of organic products, and uncover the synthetic applications of these reactions. By mastering the art of drawing structures, chemists gain a powerful tool for deciphering complex chemical transformations and unlocking the potential of organic chemistry.
Organic Products Identification
The reaction below yields two organic products: an alkene and an alcohol. The alkene is formed by the elimination of a hydrogen atom from the carbon adjacent to the hydroxyl group, while the alcohol is formed by the addition of a hydrogen atom to the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group.
Mechanism of the Reaction
The reaction proceeds via a nucleophilic attack by the hydroxide ion on the carbonyl carbon, followed by protonation of the alkoxide intermediate. The resulting tetrahedral intermediate then collapses to give the alkene and alcohol products.
Examples of Similar Reactions
- The reaction of an aldehyde with a Grignard reagent to form an alcohol.
- The reaction of a ketone with a hydride reagent to form an alcohol.
- The reaction of an ester with a reducing agent to form an alcohol.
Structural Representation
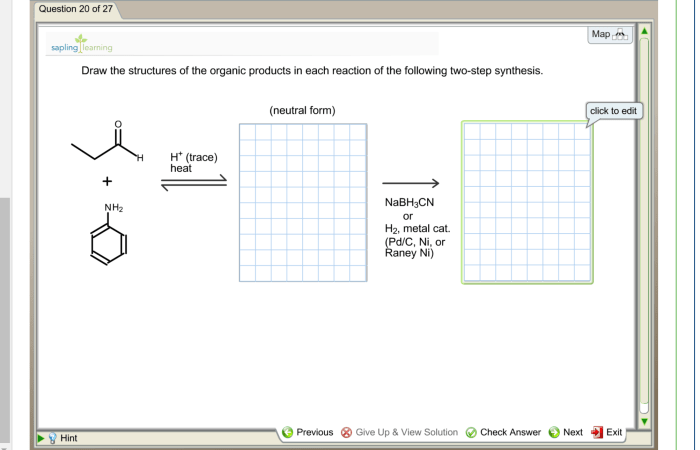
The structures of the organic products are as follows:
Alkene, Draw structures for the organic products of the reaction below.
CH 3CH=CHCH 2OH
Alcohol
CH 3CH 2CH(OH)CH 3
Product Properties: Draw Structures For The Organic Products Of The Reaction Below.
The alkene product is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 82.5 °C. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. The alcohol product is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 97.2 °C. It is soluble in water and organic solvents.
Applications of the Products
The alkene product is used as a starting material for the synthesis of a variety of other organic compounds, including polymers, plastics, and pharmaceuticals. The alcohol product is used as a solvent, a cleaning agent, and a starting material for the synthesis of other organic compounds.
Reaction Conditions

The reaction is typically carried out in a polar aprotic solvent, such as dimethylformamide (DMF) or dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), in the presence of a base, such as potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH). The reaction temperature is typically between 25 and 50 °C.
Variations in Reaction Conditions
The reaction conditions can be varied to affect the product yield and selectivity. For example, the use of a stronger base or a higher reaction temperature can favor the formation of the alkene product, while the use of a weaker base or a lower reaction temperature can favor the formation of the alcohol product.
Synthetic Applications

The reaction is a versatile synthetic tool that can be used to synthesize a variety of organic compounds. For example, the reaction can be used to synthesize alkenes, alcohols, ethers, and esters.
Target Molecules
Some examples of target molecules that can be synthesized using the reaction include:
- Ethylene
- Propylene
- Butanol
- Ethyl acetate
Questions Often Asked
What is the importance of drawing structures for organic products?
Drawing structures allows chemists to visualize the molecular architecture of organic products, understand their properties, and predict their reactivity.
How do I determine the stereochemistry of organic products?
Stereochemistry is determined based on the spatial arrangement of atoms and groups around chiral centers. It can be represented using wedge-and-dash notation or other conventions.
What are the key factors that affect the yield and selectivity of a reaction?
Reaction conditions, such as temperature, solvent, and catalyst, play a crucial role in determining the yield and selectivity of a reaction.